Prosthetic Arm
March 2021 - April 2021
- Tech Stack: SolidWorks, Additive Manufacturing, Arduino Uno, C++
- Summary
Developed a CAD model and functional prototype of a cost-effective Prosthetic Arm using Additive Manufacturing and Arduino Uno.
Performed Topology Optimization using SolidWorks to reduce the material cost.
My role: CAD, helped with Arduino programming
- In-Depth
Introduction
The idea behind the project was to design and develop a cost-effective Prosthetic Arm. The cost was reduced by using less material to make the structure of the arm. Topology Optimization was performed to determine the non-critical portions of the structure, and hence remove them. This reduced the material used and hence reduced the cost. The prototype was made using 3-D Printing, Arduino Uno and an EMG kit.
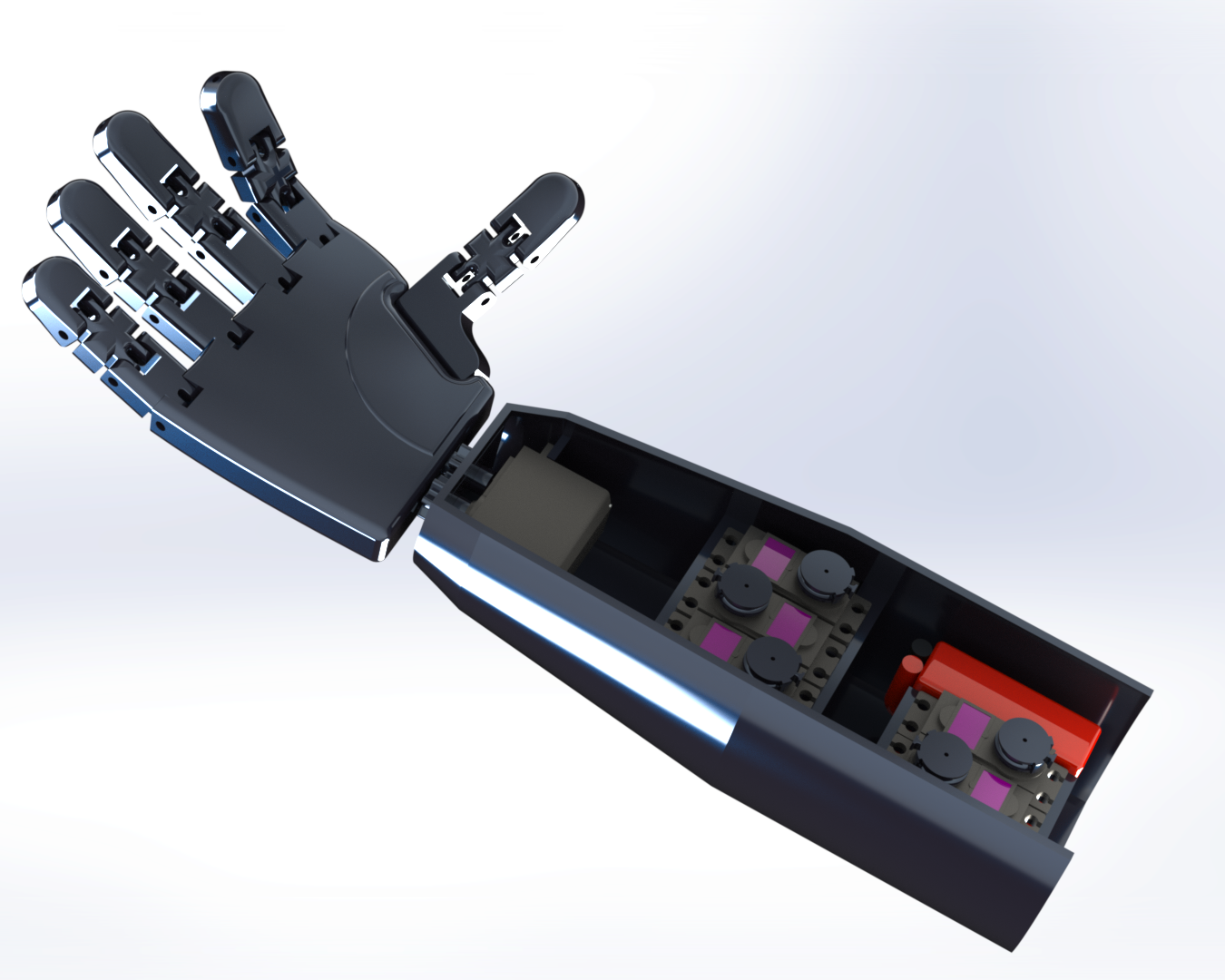
Fig-1 Rendered Image of the Prosthetic Arm 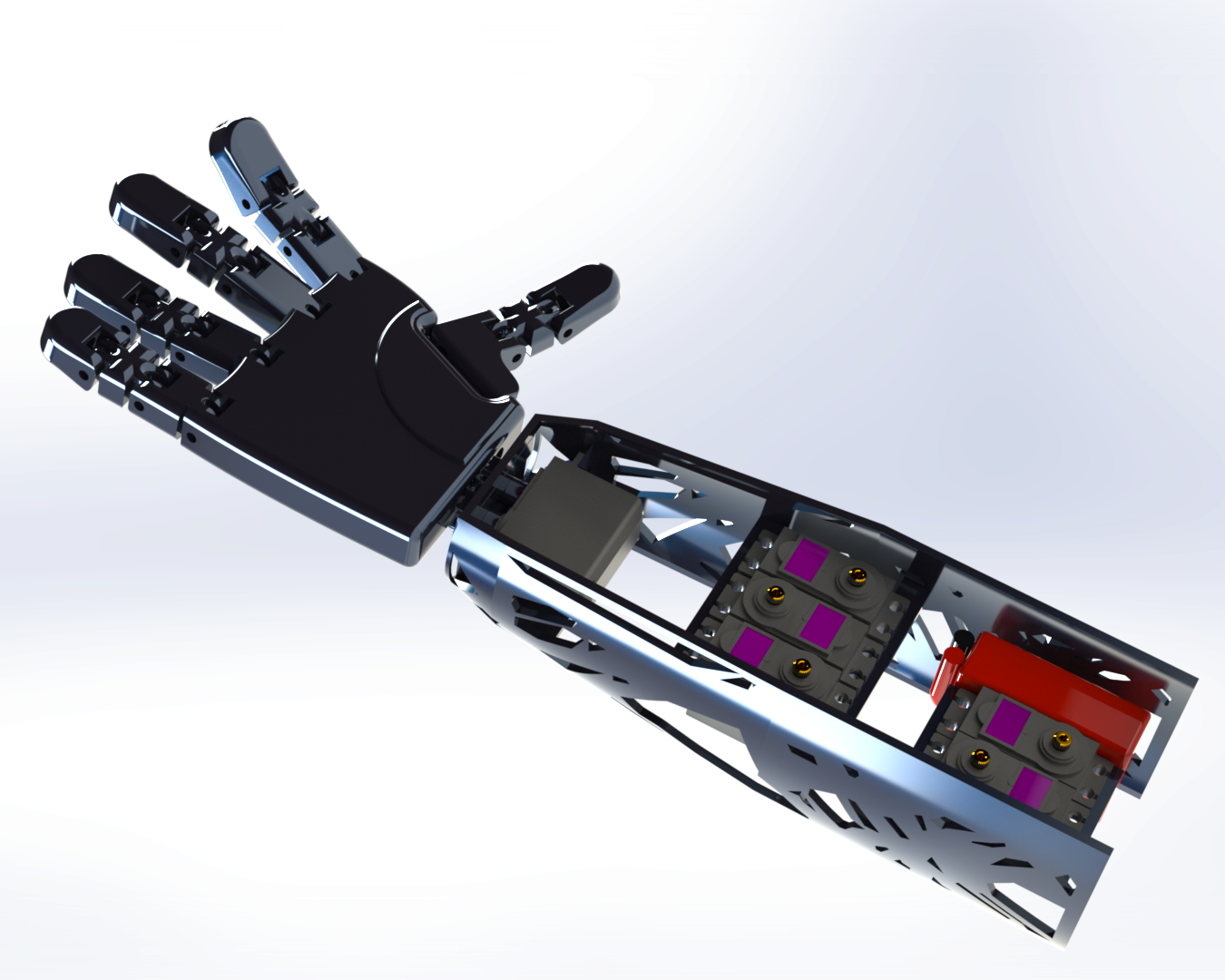
Fig-2 Rendered Image of the Prosthetic Arm after Topology Optimization Motivation
The goal of the project was to design a cost-effective Prosthetic Arm. Prosthetic Arms can get quite expensive, and are hence beyond the reach of the general masses. Thus, this motivated us to try and reduce the cost of such arms, so that it becomes more accessible to people.Mechanical Design
The components of the Prosthetic Arm were made using 3-D Printing. It has 6 Degrees of Freedom. Each finger is attached to a servo motor via a tendon. Once a motor actuates, it pulls on the tendon, creating tension, which causes the corresponding finger to move. The individual digits of each finger cannot be actuated separately, and the entire finger moves as whole. The wrist joint is controlled via a sixth servo motor, and is connected via a 1:1 gear. The motors receive signals from the user's arm, via an Electromyography (EMG) sensor, which senses electrical impulses sent from our brain to muscles in the body.
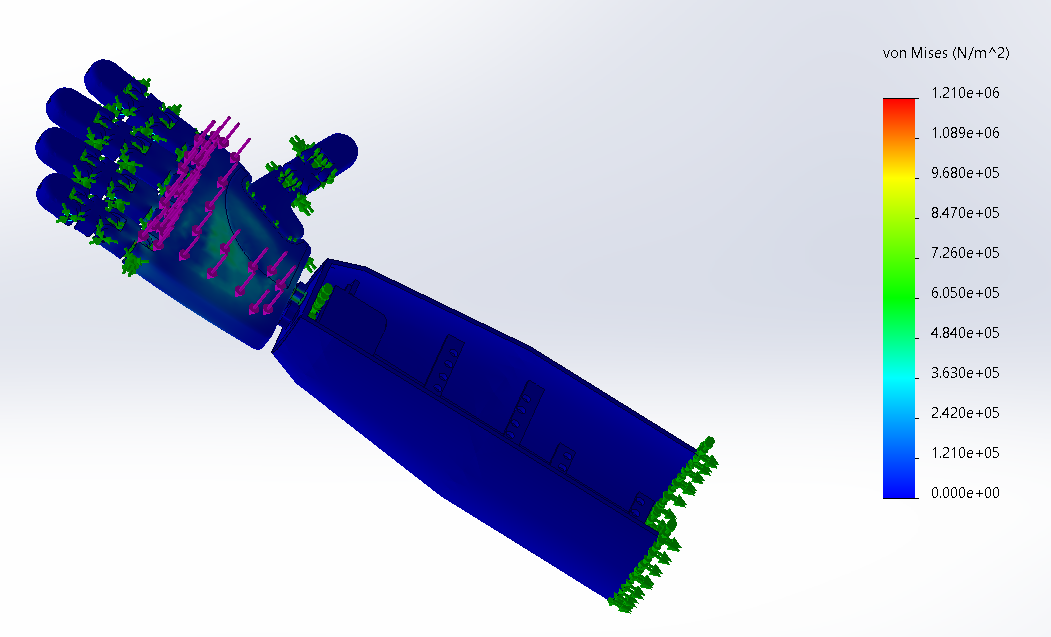
Fig-3 Stress Analysis - Von Mises 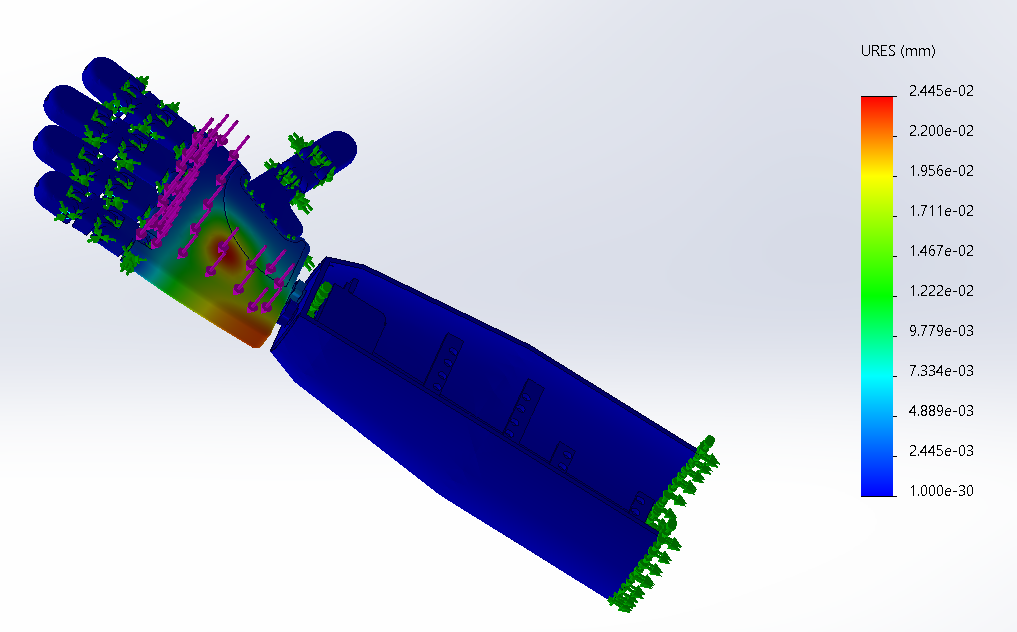
Fig-4 Stress Analysis - Displacement Topology Optimization
Topology Optimization was done to reduce the material used. The criteria used were to minimise mass by 30%, and ensure that the displacement does not increase by more than 1.2 times. The forearm and the hand were optimized, as they were the largest and most prominent components of the arm, and were also the main load bearing parts of the arm. The total mass reduction was 17.35%.
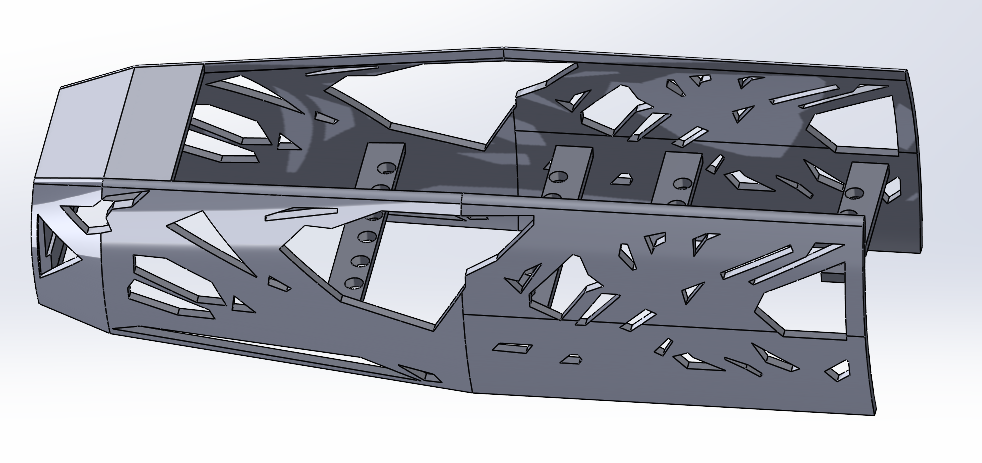
Fig-5 The Forearm after Topology Optimization 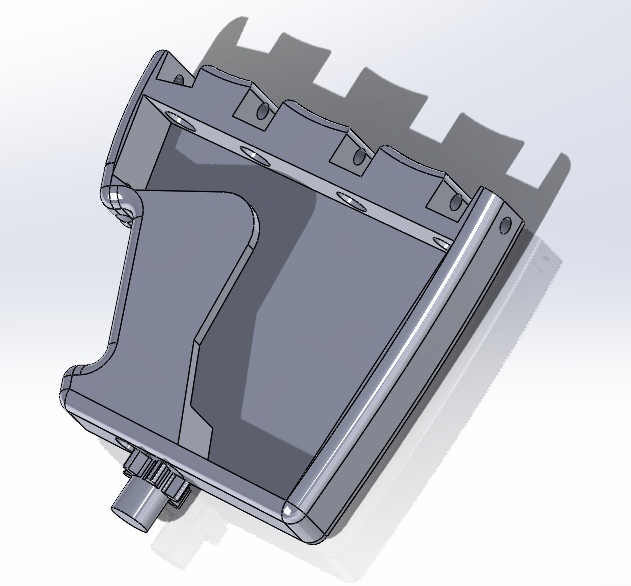
Fig-6 The Hand after Topology Optimization - Results
Topology Optimization was successfully used to reduce the material cost of the arm by 18%. However, considering that the arm has been 3-D Printed using PLA, it is relatively weak, and can only be utilized for manipulating light objects like soda cans, stationery etc. Strength can be improved by either changing the material, or changing the manufacturing method, both of which will increase cost.
